Xét các số thực x,y thỏa mãn
Câu hỏi :
Xét các số thực x,y thỏa mãn \[{2^{{x^2} + {y^2} + 1}} \le ({x^2} + {y^2} - 2x + 2){4^x}\]. Giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức \[P = \frac{{8x + 4}}{{2x - y + 1}}\;\] là \[a + \sqrt a \].Tìm a
* Đáp án
* Hướng dẫn giải
Bước 1: Chia cả 2 vế của bất phương trình cho\[{4^x}\] và đặt \[t = {x^2} + {y^2} - 2x + 1\]
Nhận xét:\[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x + 2 = {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2} + 1 > 0\,\,\,\forall x,y\]
Bpt \[ \Leftrightarrow {2^{{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x + 1}} \le {x^2} + {y^2} - 2x + 2\]
Đặt\[t = {x^2} + {y^2} - 2x + 1\] bất phương trình trở thành\[{2^t} \le t + 1 \Leftrightarrow {2^t} - t - 1 \le 0\]
Bước 2: Xét hàm đặc trưng\[f\left( t \right) = {2^t} - t - 1\] và đánh giá t từ đó đánh giá\[{\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2}\]
Xét hàm số\[f\left( t \right) = {2^t} - t - 1\] có\[f'\left( t \right) = {2^t}\ln 2 - 1 = 0 \Leftrightarrow t = {\log _2}\left( {{{\log }_2}e} \right).\]
BBT:
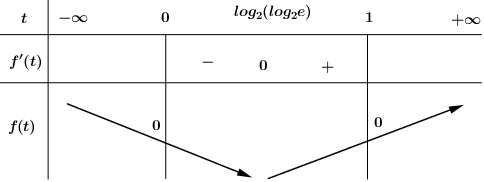
Suy ra ta có\[0 \le t \le 1 \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2} \le 1\]
Bước 3: Biến đổi P và tìm min, max
Ta có:
\[P = \frac{{8x + 4}}{{2x - y + 1}} \Leftrightarrow 2Px - Py + P = 8x + 4\]
\[ \Leftrightarrow P - 4 = \left( {8 - 2P} \right)x + Py \Leftrightarrow 3P - 12 = \left( {8 - 2P} \right)\left( {x - 1} \right) + Py\]
\[ \Leftrightarrow {\left( {3P - 12} \right)^2} \le \left[ {{{\left( {8 - 2P} \right)}^2} + {P^2}} \right]\left[ {{{\left( {x - 1} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {3P - 12} \right)^2} \le {\left( {8 - 2P} \right)^2} + {P^2} \Leftrightarrow 4{P^2} - 40P + 80 \le 0\]
\[ \Leftrightarrow 5 - \sqrt 5 \le P \le 5 + \sqrt 5 \]
Bước 4: Xét dấu “=” xảy ra
Dấu “=” xảy ra
\(\begin{array}{l} \Leftrightarrow \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\frac{{8 - 2P}}{P} = \frac{{x - 1}}{y} = - \frac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}}\\{{{(x - 1)}^2} + {y^2} = 1}\end{array}} \right. \Leftrightarrow \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x - 1 = - \frac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}y}\\{\frac{9}{5}{y^2} = 1}\end{array}} \right.\\ \Leftrightarrow \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{x = 1 \mp \frac{2}{3}}\\{y = \pm \frac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}}\end{array}} \right.\end{array}\)
\[ \Rightarrow \max P = 5 + \sqrt 5 \] đạt được khi\[x = \frac{1}{3};y = \frac{{\sqrt 5 }}{3}\]
Vậy a=5
Câu hỏi trên thuộc đề trắc nghiệm dưới đây !
Bất phương trình logarit !!
Copyright © 2021 HOCTAP247
